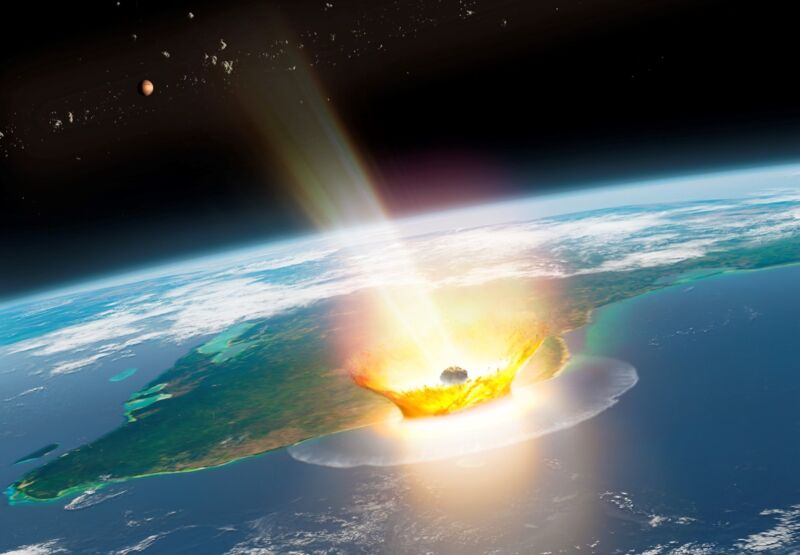
Enlarge / Artist impression of a large asteroid impacting on Earth, such as the Chicxulub event that caused the end-Cretaceous mass extinction 66 million years ago. (credit: Mark Garlick)
Some 66 million years ago, an errant asteroid wiped out three-quarters of all plant and animal species on Earth, most notably taking down the dinosaurs. That has long been the scientific consensus. However, three years ago, Harvard astronomers offered an alternative hypothesis: The culprit may have been a fragment of a comet thrown off-course by Jupiter’s gravity and ripped apart by the Sun.
Now an international team of scientists have reaffirmed the original hypothesis, according to a new paper published in the journal Science. They analyzed ruthenium isotopes from the Chicxulub impact crater and concluded the impact was due to a carbonaceous-type asteroid, likely hailing from beyond Jupiter.
As previously reported, the most widely accepted explanation for what triggered that catastrophic mass extinction is known as the “Alvarez hypothesis,” after the late physicist Luis Alvarez and his geologist son, Walter. In 1980, they proposed that the extinction event may have been caused by a massive asteroid or comet hitting the Earth. They based this conclusion on their analysis of sedimentary layers at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary (the K-Pg boundary, formerly known as the K-T boundary) found all over the world, which included unusually high concentrations of iridium—a metal more commonly found in asteroids than on Earth. (That same year, Dutch geophysicist Jan Smit independently arrived at a similar conclusion.)
Read 8 remaining paragraphs | Comments