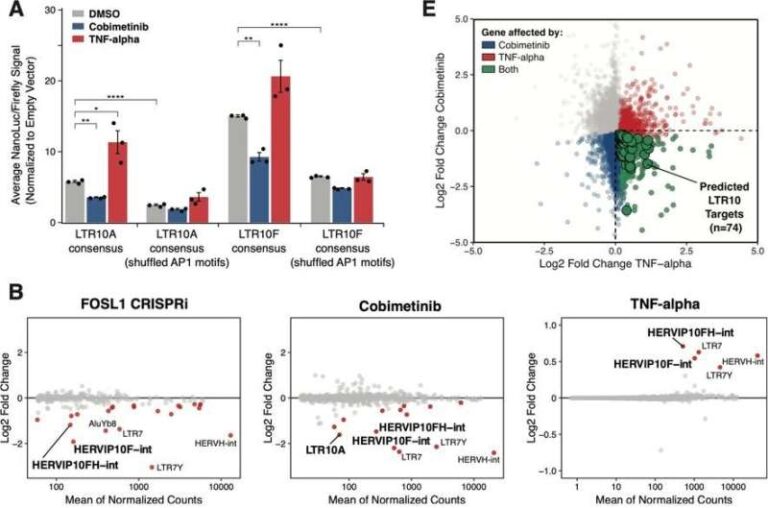
Although tiny, peatland microorganisms have a big impact on climate

Polyphenols are generally toxic to microorganisms. In peatlands, scientists thought microorganisms avoided this toxicity by degrading polyphenols using an oxygen-dependent enzyme, and thus that low-oxygen conditions inhibit microbes’ carbon cycling. However, a new study found that Arctic peatland microorganisms used…