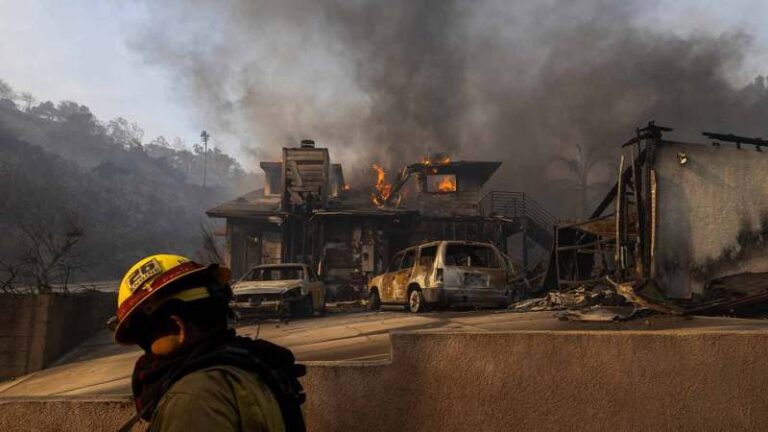
Did plate tectonics give rise to life? Groundbreaking new research could crack Earth’s deepest mystery.

Emerging evidence suggests that plate tectonics, or the recycling of Earth’s crust, may have begun much earlier than previously thought — and may be a big reason that our planet harbors life.