A nuclear clock prototype hints at ultraprecise timekeeping
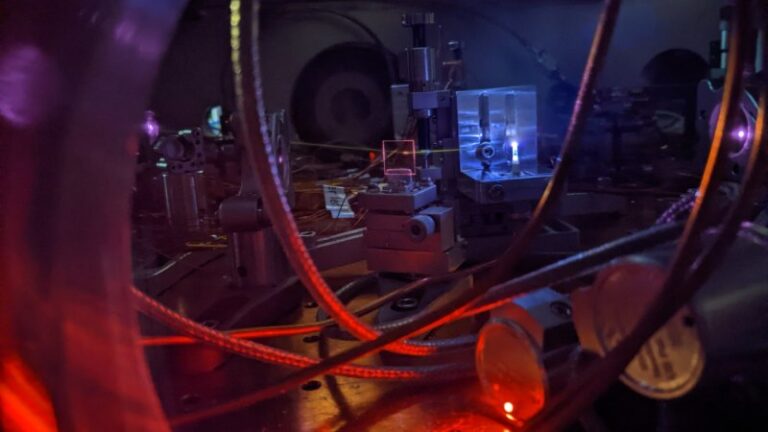
Nuclear clocks could rival atomic clocks and allow for new tests of fundamental physics. A new experiment demonstrates all the ingredients needed.
Science and Technolgy blog

Nuclear clocks could rival atomic clocks and allow for new tests of fundamental physics. A new experiment demonstrates all the ingredients needed.
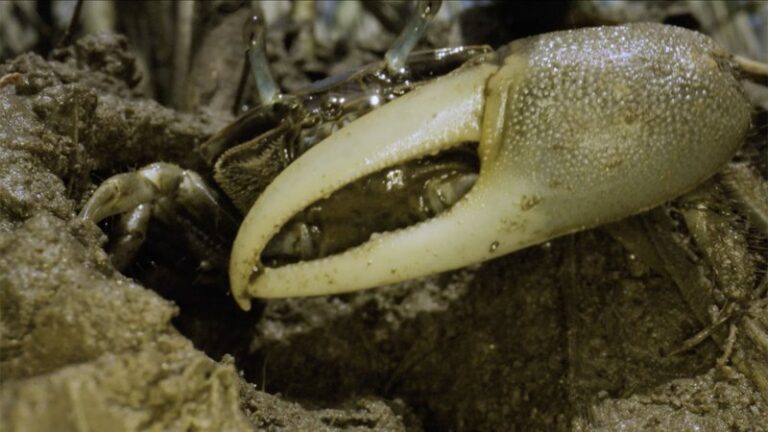

The crabs are climate migrants and could be a harbinger of changes to come as more species move in.
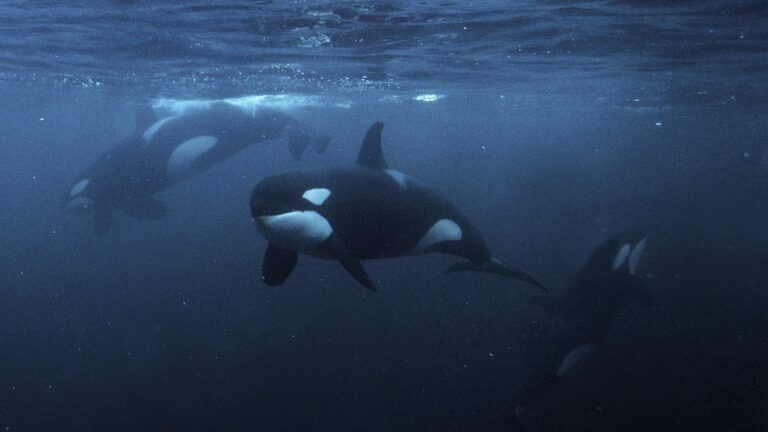

Orcas off the coasts of Spain and Portugal may be using boats as targets to practice hunting their favorite food, Atlantic bluefin tuna.
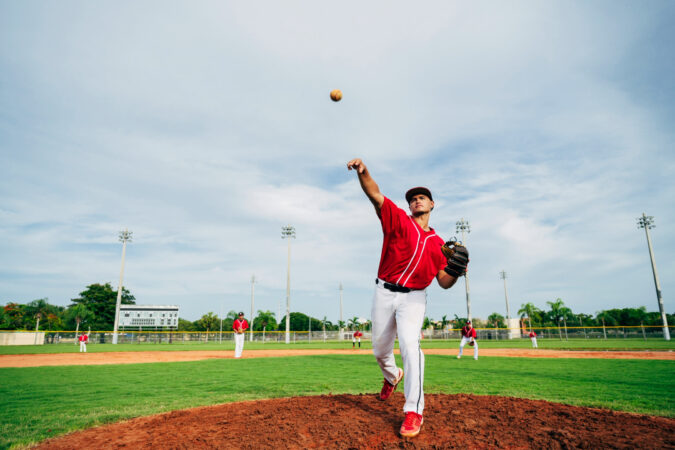

Each year, 2 million Americans injure their shoulder’s rotator cuff. That includes many teens, who may hurt their shoulder while participating in sports, such as baseball, volleyball and swimming. Many of these injuries are hard to treat. Only about one…
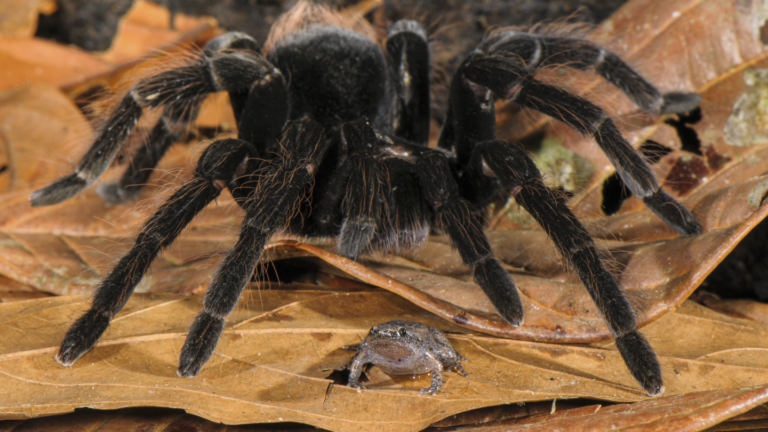

Tarantulas’ hairy bodies protect against the scavenging, spider-eating army ants that clean their nests, scientists say.
Scientists in China have developed a tensor processing unit (TPU) that uses carbon-based transistors instead of silicon – and they say it’s extremely energy efficient.
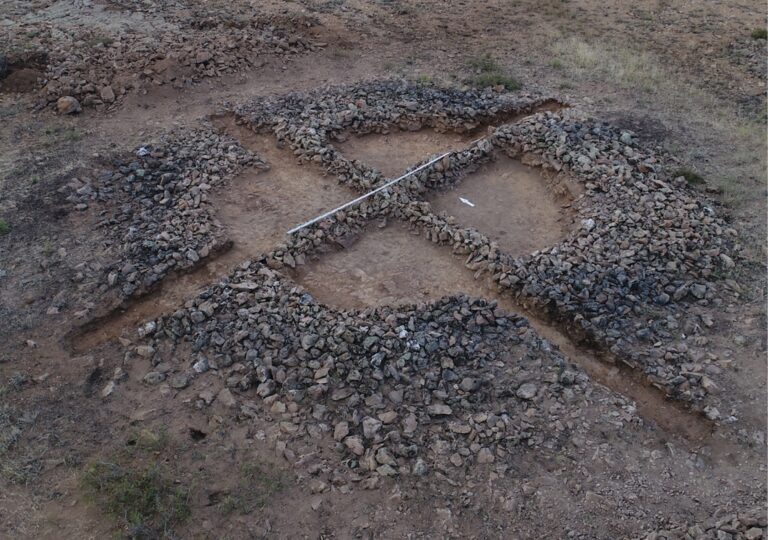

Archaeologists in Kazakhstan have discovered 10 kurgans, or burial mounds, dating to the Middle Ages, and some have “mustaches.”
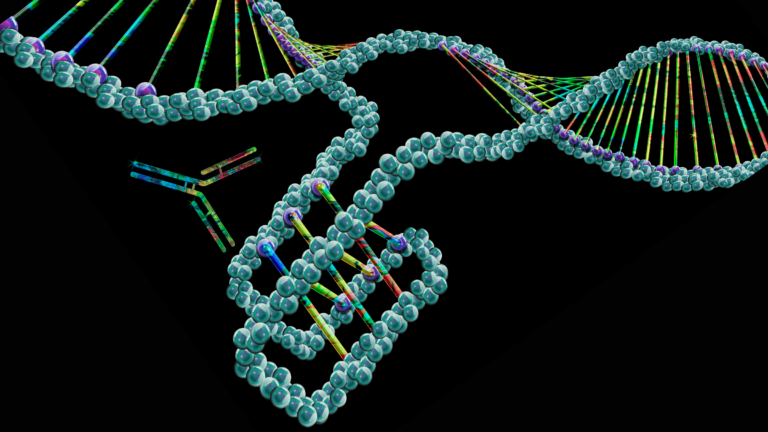
The mapping of 50,000 mysterious “knots” in the human genome may someday lead to the development of new cancer drugs, researchers say.
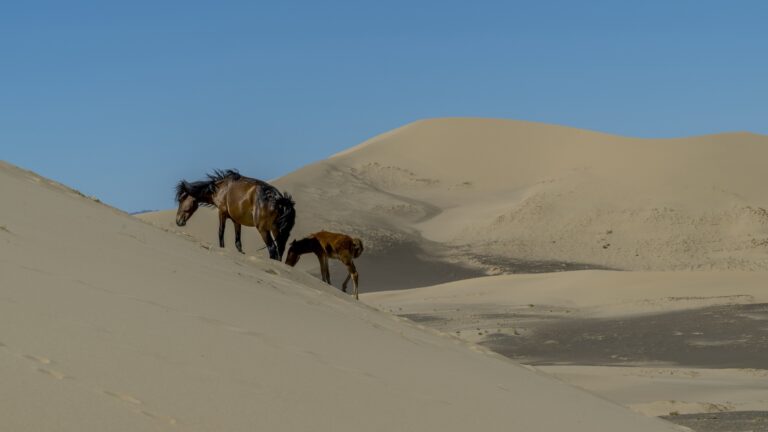

New analyses of bones, teeth, genetics and artifacts suggest it’s time to revise a long-standing hypothesis for how humans domesticated horses.
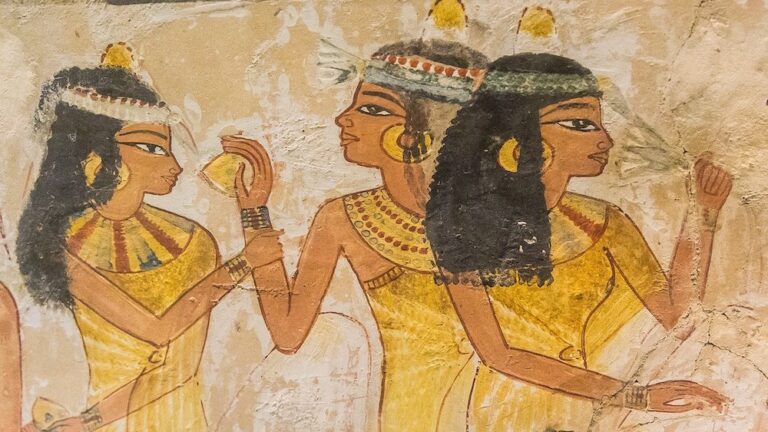

Archaeologists remain uncertain about the purpose of these head cones, but it appears that ancient Egyptians associated them with “sensuality, sexuality and related notions.”