FDA bans red dye No. 3 in food
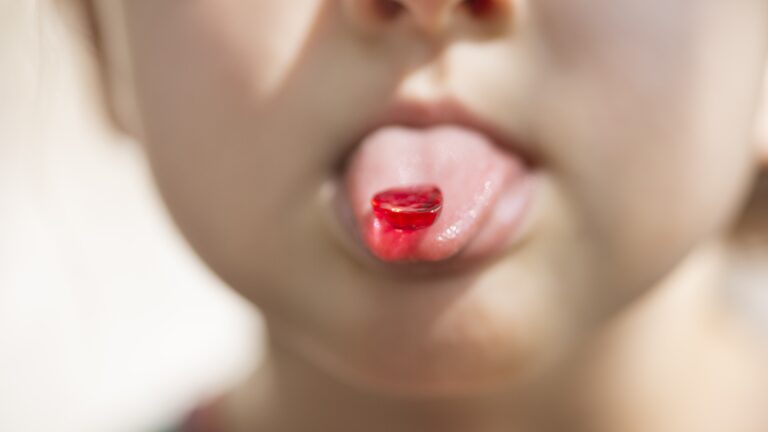

The FDA will no longer allow red dye No. 3 in foods or ingested drugs, citing evidence that high doses of the dye can cause cancer in male rats. There is no evidence it’s carcinogenic in humans.
Science and Technolgy blog

The FDA will no longer allow red dye No. 3 in foods or ingested drugs, citing evidence that high doses of the dye can cause cancer in male rats. There is no evidence it’s carcinogenic in humans.

The Bárðarbunga volcano system was responsible for Iceland’s largest eruption for 300 years back in 2014. After a recent increase in seismic activity, could it be about to erupt again?

The bone fragments were once thought to be some of the oldest human fossils found in Japan.

Antarctica’s Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf may be under threat due to relatively warm water from the deep sea flowing towards the shelf. Is climate change to blame?
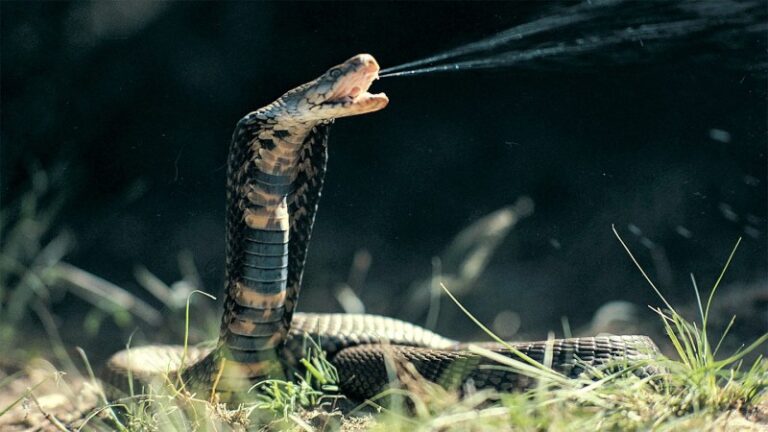

The current way to produce antivenoms is antiquated. Experiments in mice suggest that an artificial intelligence approach could save time and money.
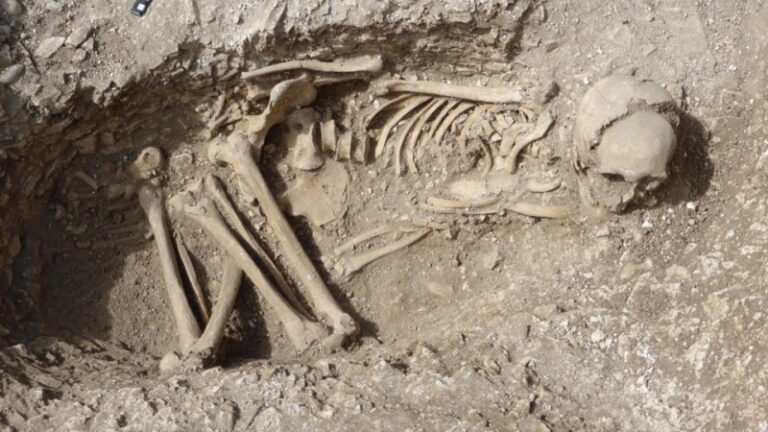

Ancient DNA indicates women stayed in their home communities and married partners from outside the area.
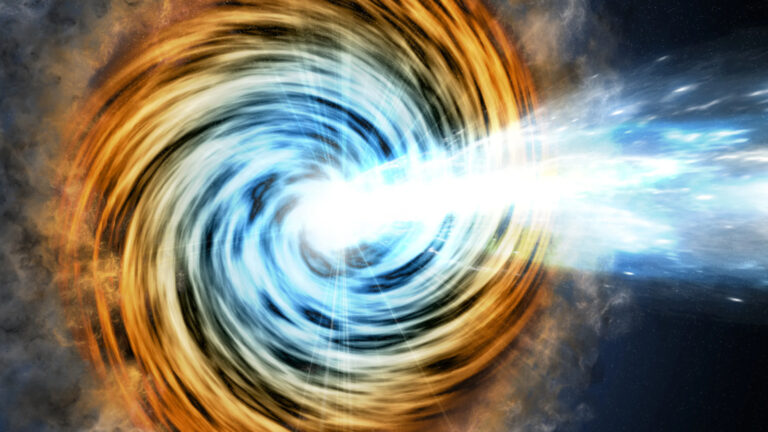

The newly discovered “blazar,” which has a mass equal to 700 million suns, is the oldest of its kind ever seen and changes what we know about the early universe.
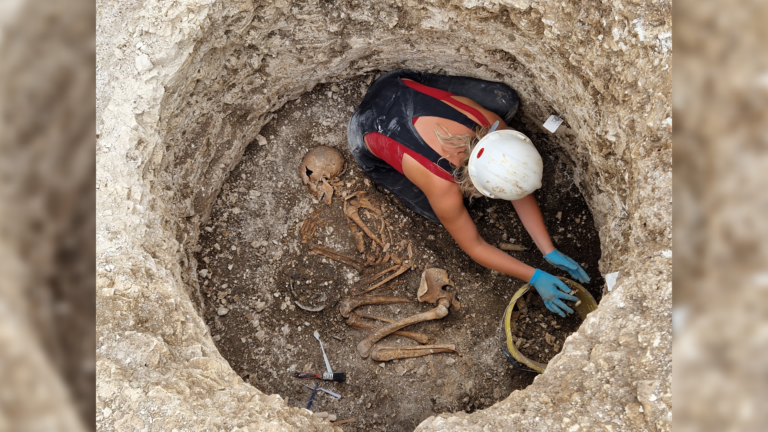

An analysis of dozens of British Iron Age skeletons has revealed that Celtic society was organized around women.
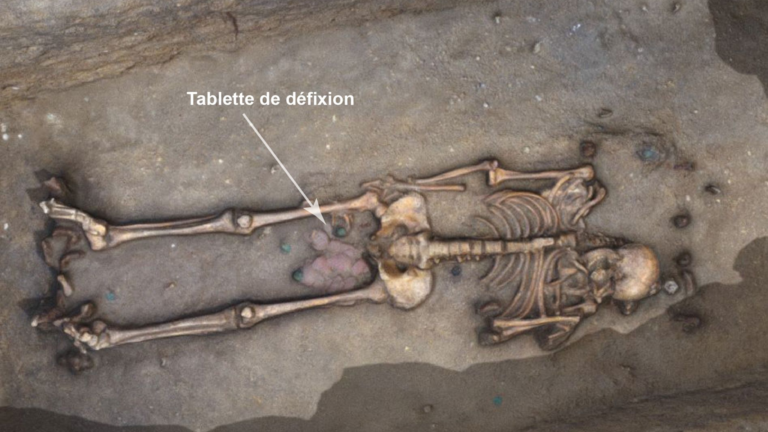
Excavation of a Roman-era cemetery in France yielded nearly two dozen lead tablets inscribed in Latin and Gaulish.
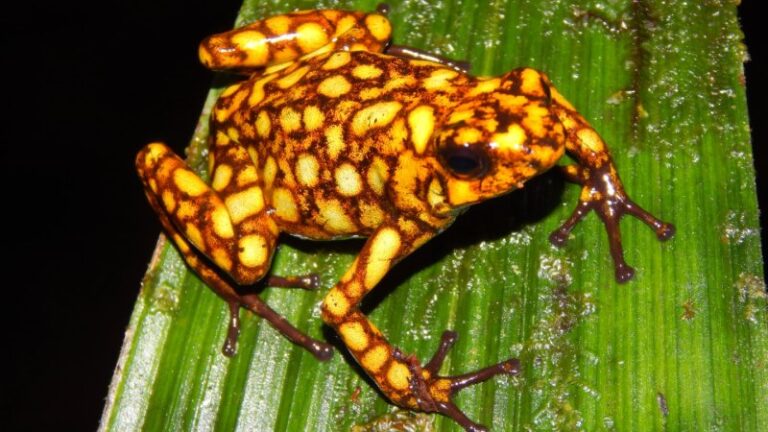

Toxins on poison dart frog skin mold the skin’s microbial community, boosting species variety and potentially even feeding some daredevil bacteria.