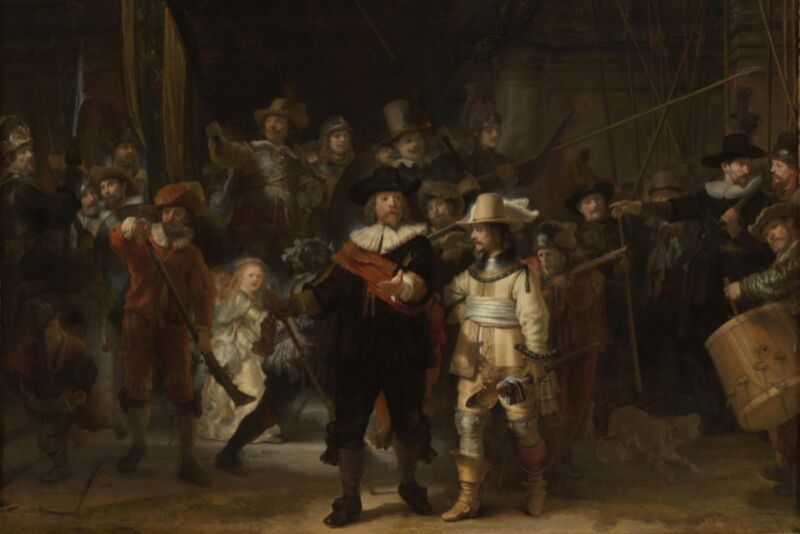
Enlarge / Rembrandt’s The Night Watch underwent many chemical and mechanical alterations over the last 400 years. (credit: Public domain)
Since 2019, researchers have been analyzing the chemical composition of the materials used to create Rembrandt’s masterpiece, The Night Watch, as part of the Rijksmuseum’s ongoing Operation Night Watch, devoted to its long-term preservation. Chemists at the Rijksmuseum and the University of Amsterdam have now detected unusual arsenic-based yellow and orange/red pigments used to paint the duff coat of one of the central figures in the painting, according to a recent paper in the journal Heritage Science. It’s a new addition to Rembrandt’s known pigment palette that further adds to our growing body of knowledge about the materials he used.
As previously reported, past analyses of Rembrandt’s paintings identified many pigments the Dutch master used in his work, including lead white, multiple ochres, bone black, vermilion, madder lake, azurite, ultramarine, yellow lake, and lead-tin yellow, among others. The artist rarely used pure blue or green pigments, with Belshazzar’s Feast being a notable exception. (The Rembrandt Database is the best resource for a comprehensive chronicling of the many different investigative reports.)
Early last year, the researchers at Operation Night Watch found rare traces of a compound called lead formate in the painting—surprising in itself, but the team also identified those formates in areas where there was no lead pigment, white or yellow. It’s possible that lead formates disappear fairly quickly, which could explain why they have not been detected in paintings by the Dutch Masters until now. But if that is the case, why didn’t the lead formate disappear in The Night Watch? And where did it come from in the first place?
Read 11 remaining paragraphs | Comments