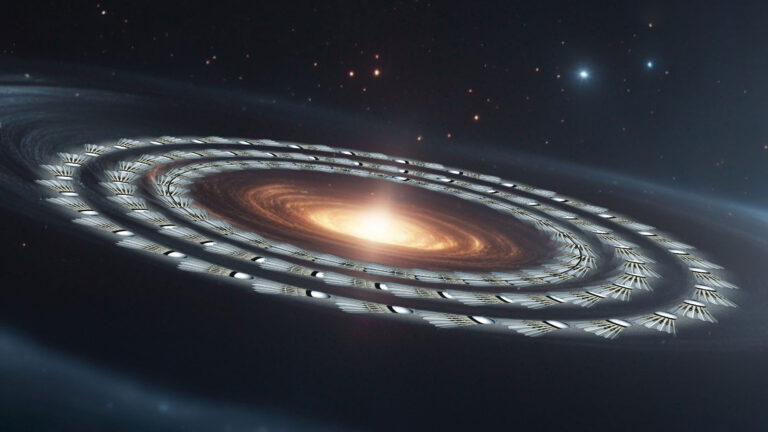
The birth of a planet starts with a microscopic grain floating in a protoplanetary disk, a swirling cloud of gas and other particles surrounding a young star. How the gas and dust interact has implications for the formation of new worlds.
“Those teeny grains—those are the building blocks of planets,” said Zhe-Yu Daniel Lin, an astrophysicist at the Carnegie Institution for Science. He describes the shape of the grains as “potatoes.”
It’s hot and breezy in the interstellar cloud, but it’s not entirely chaotic. Astronomical observations have found that the grains, instead of tumbling through space, are oriented neatly along their orbital trajectories. To explain how the grains float in formation, new research led by Lin leans on the working principle behind an Earthly object: the badminton shuttle.